By default, Windows uses the DNS servers that your Wi-Fi router or LAN uses. However, if those DNS servers are slow and unreliable, you may want to switch to a better, faster DNS server on Windows 11.

Thankfully, changing DNS servers on Windows is relatively quick and painless. In this post, we’ll walk you through 3 different ways to change the DNS server on Windows 11. So, let’s start.
When Should You Change It
Under ideal conditions, you wouldn’t need to change the DNS server on Windows. However, if you experience unusually slow internet speeds and errors like DNS server isn’t responding, it’s a good idea to switch to public DNS servers on Windows 11.
Further, using the default DNS server also risks your privacy as your Internet Service Provider (ISP) might be logging your browsing history.

So, if you’re looking for better internet speed or want to protect your privacy, changing your DNS servers would be a nice idea. Cloudflare, OpenDNS, and Google are some of the top options for switching to a free public DNS server.
- Cloudflare: 1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1
- Google: 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4
- OpenDNS: 208.67.222.222 and 208.67.220.220
1. Change DNS Server Using the Settings App
Windows 11 lets you access all the important settings through the new and improved Settings app, unlike its previous iterations. Here’s how you can use it to change the DNS server on your PC.
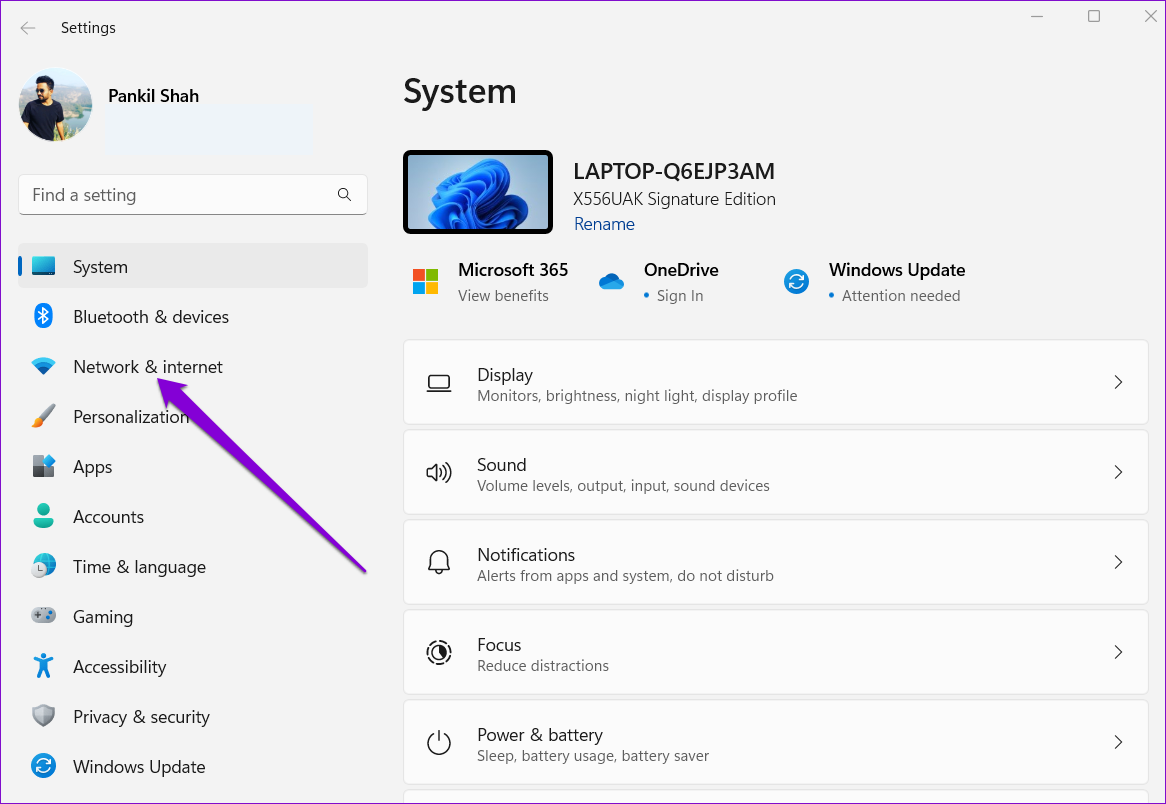
Step 1: Press the Windows key + I on your keyboard to launch the Settings app.
Step 2: Navigate to the Network & internet tab on your left.
Step 3: Click on your current internet connection type, Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
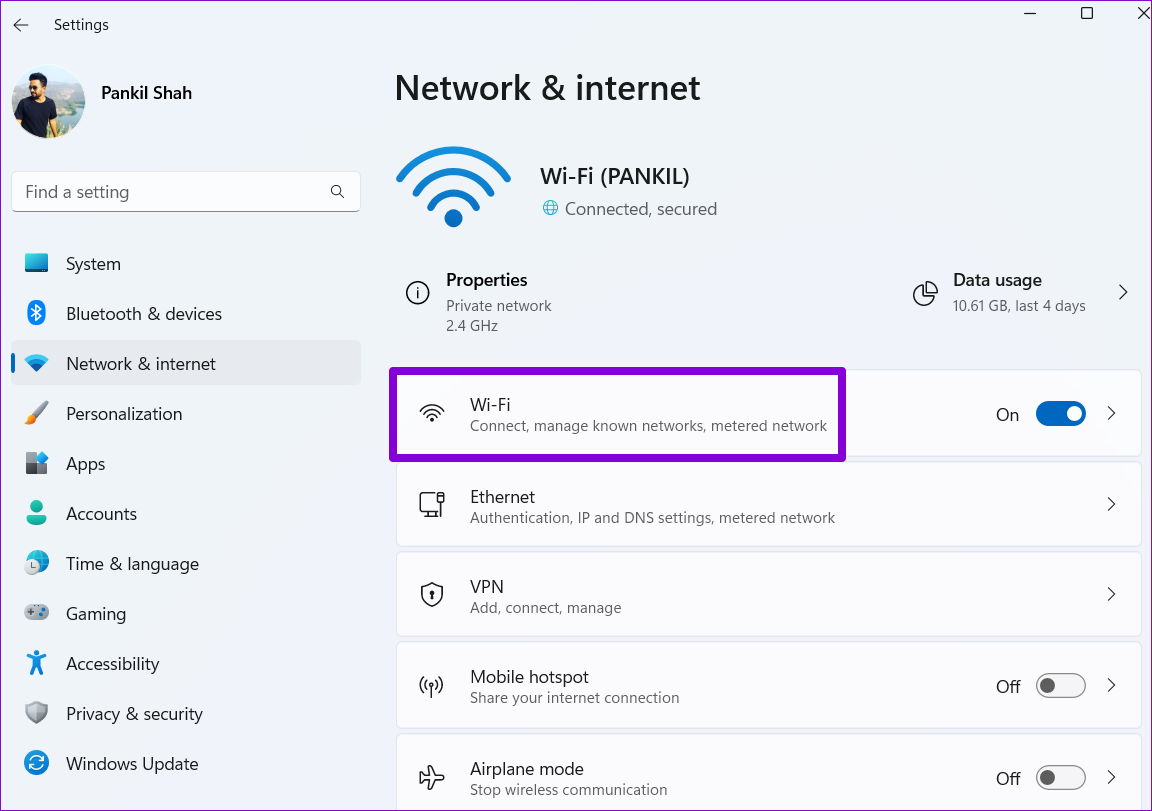
Step 4: Go to Hardware properties.
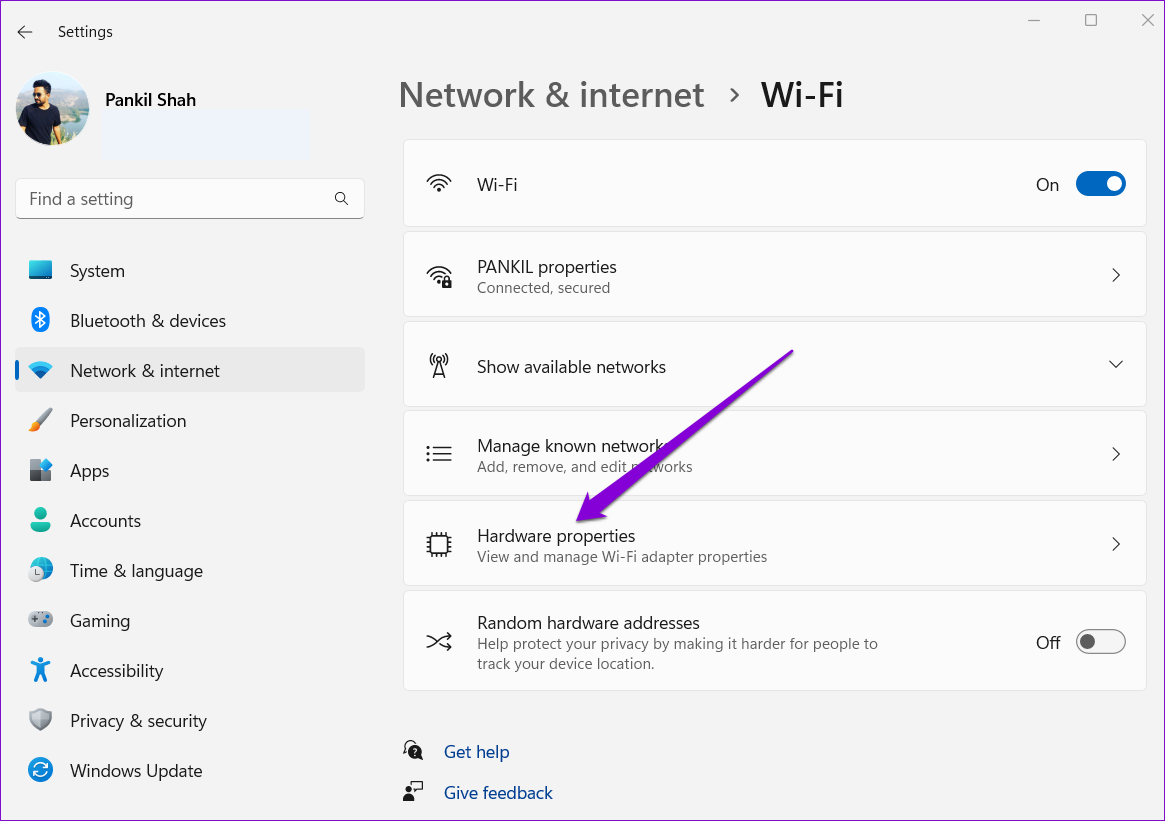
Step 5: Click on the Edit button next to DNS server assignment.
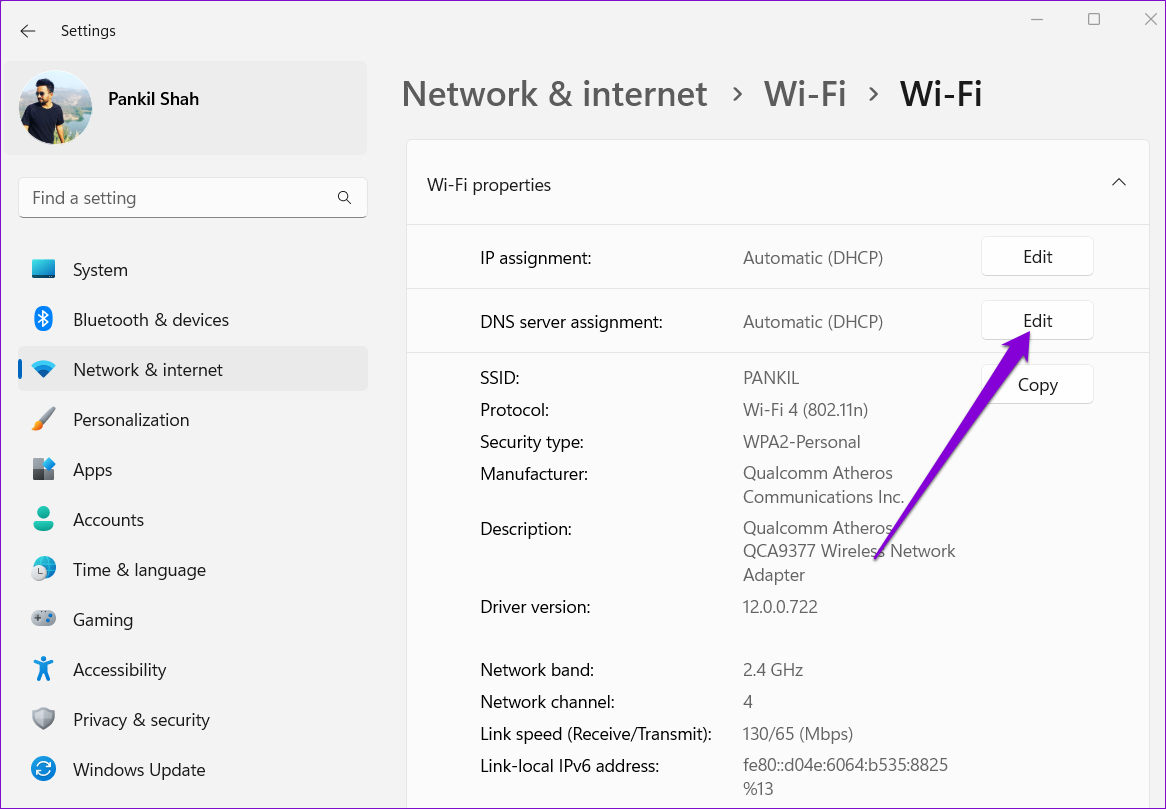
Step 6: In the Edit DNS settings window, use the drop-down menu to select Manual.

Step 7: Turn on the IPv4 or IPv6 setting, depending on the type of IP connection you wish to modify.
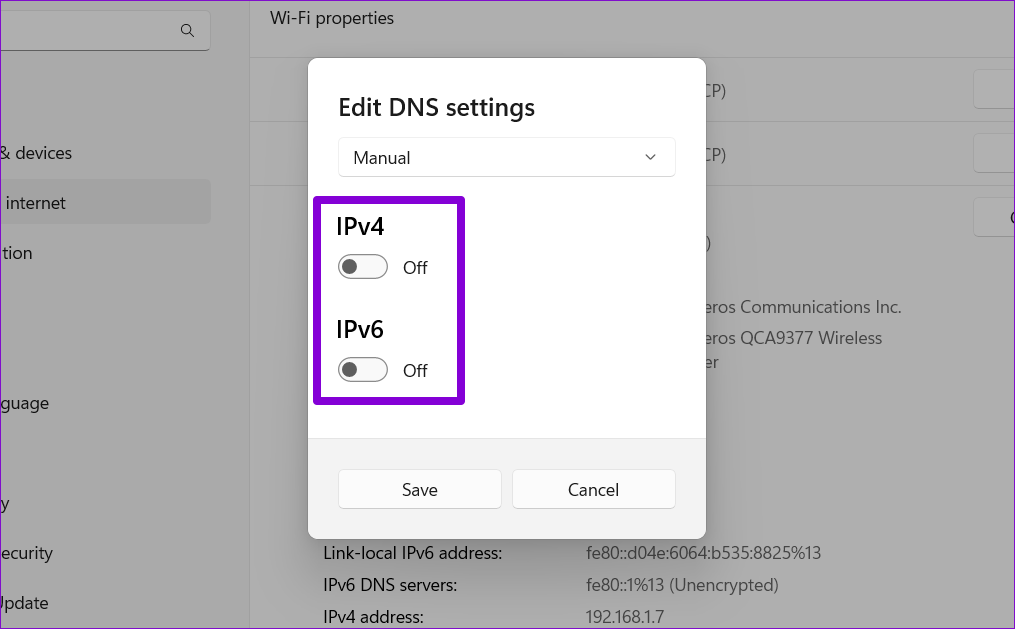
Step 8: We’ll use to Google’s public DNS servers. So you can enter 8.8.8.8 in the Preferred DNS field and 8.8.4.4 in the Alternate DNS field.
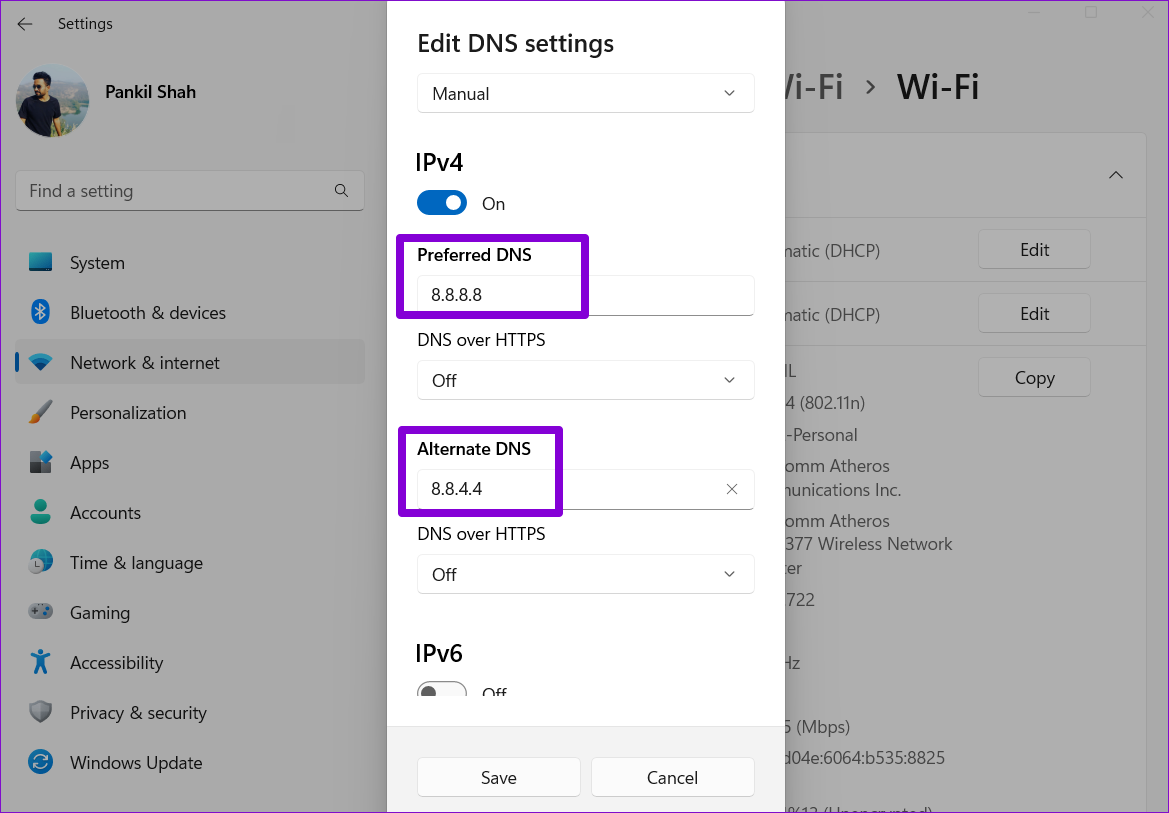
Alternatively, ou can use the drop-down menu to enable DNS over HTTPS for better privacy and security.
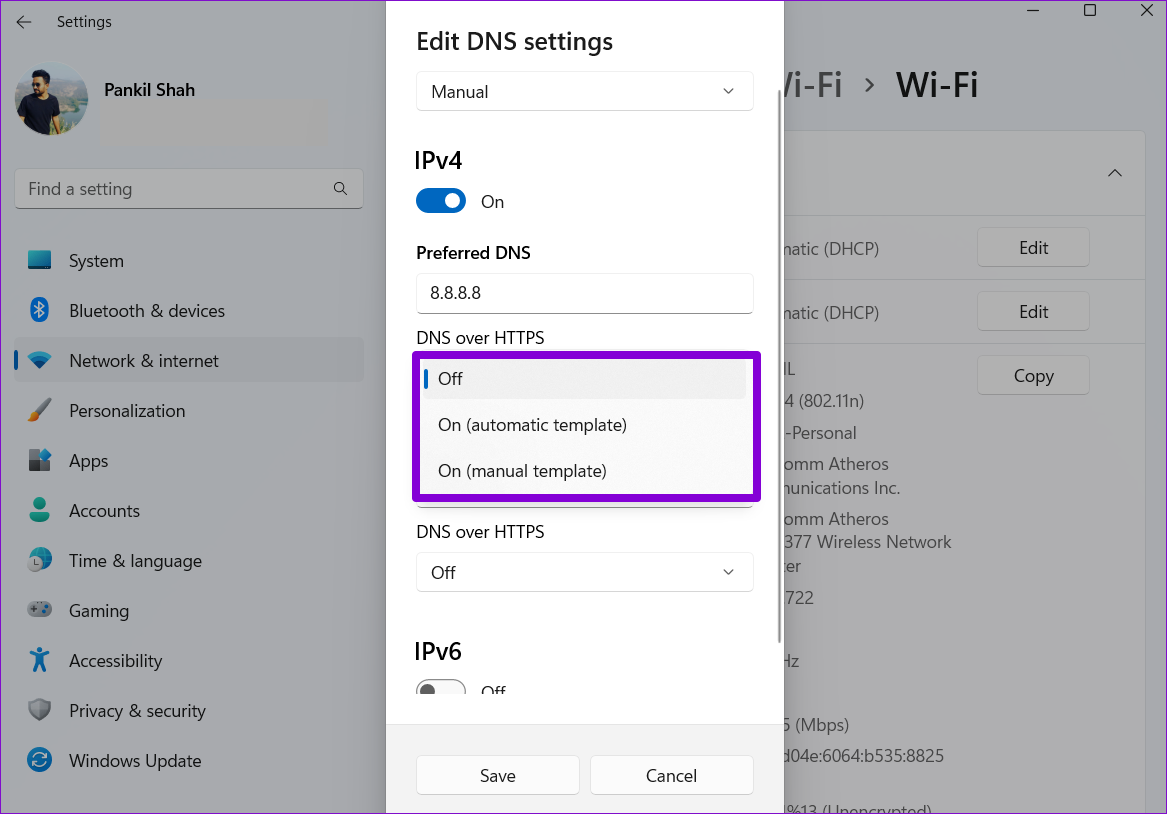
Step 9: Hit the Save button to apply changes.

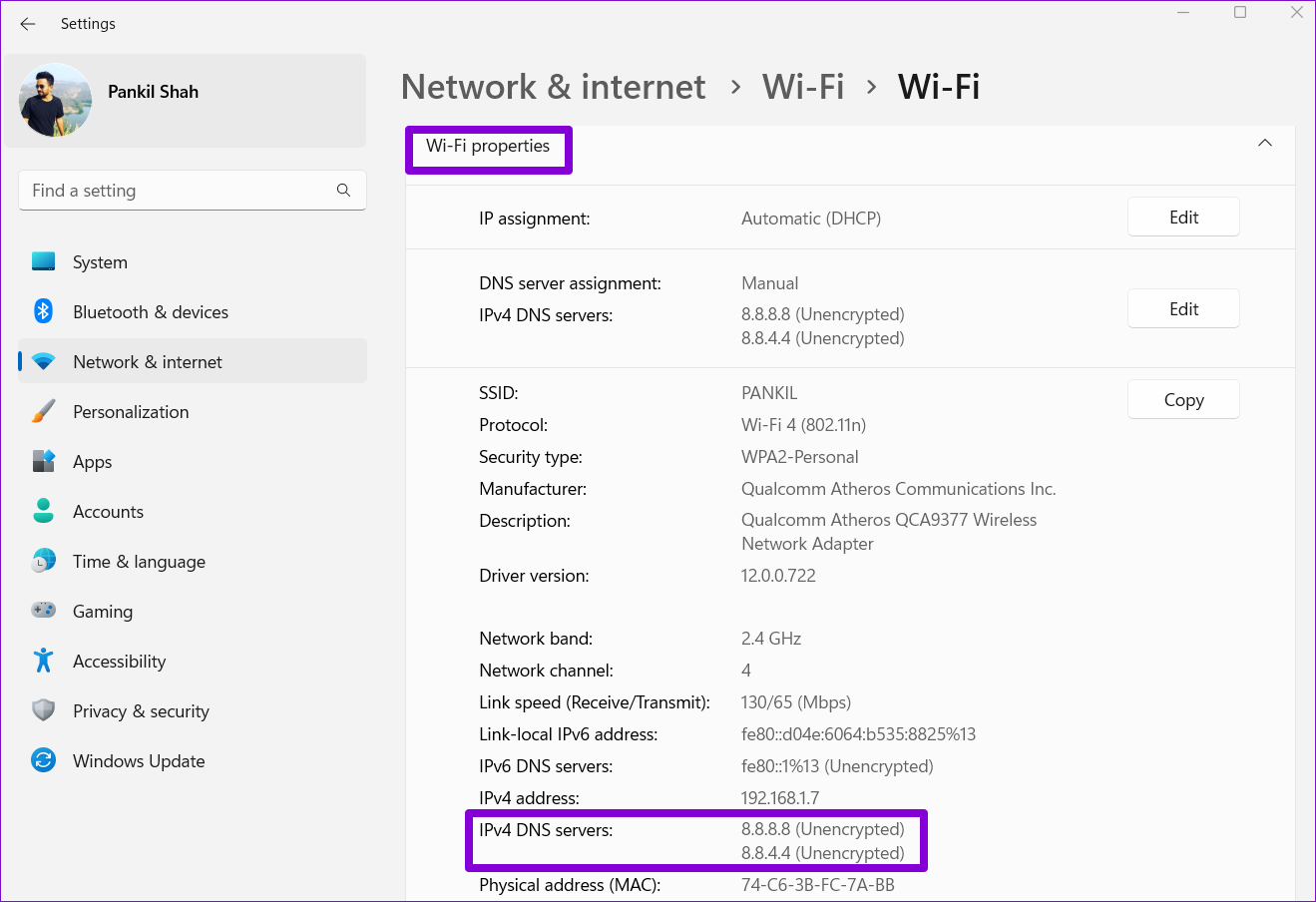
That’s about it. You’ll find your specified DNS server under Wi-Fi properties.
2. Change DNS Server Using Control Panel
If you prefer the old-school way, you can also use the Control Panel to change the DNS servers on your PC. Here’s how to do that.
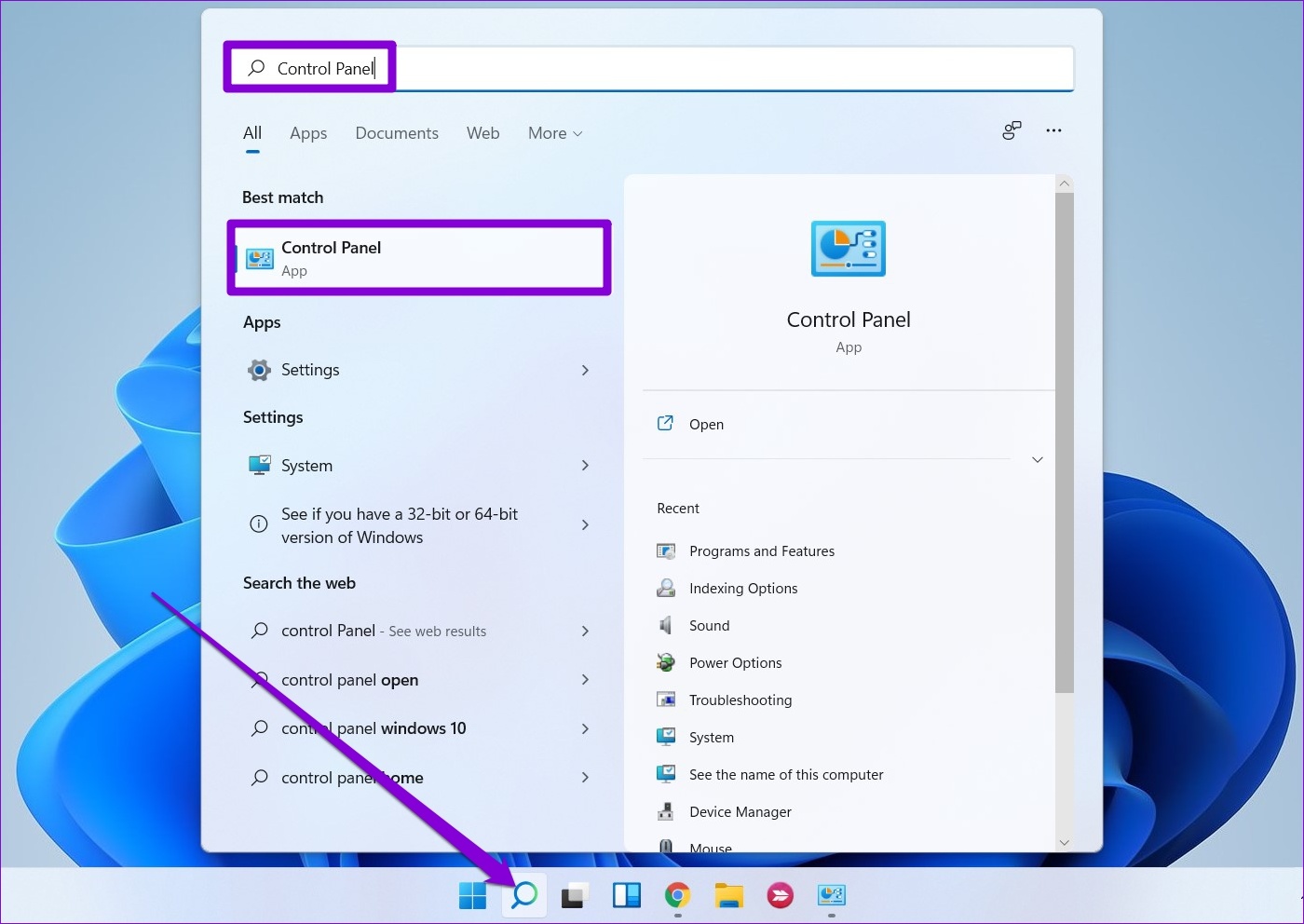
Step 1: Click on the Search icon on the Taskbar, type in control panel, and select the first result that appears.
Step 2: Use the drop-down menu in the top right corner to change the view type to large or small icons.
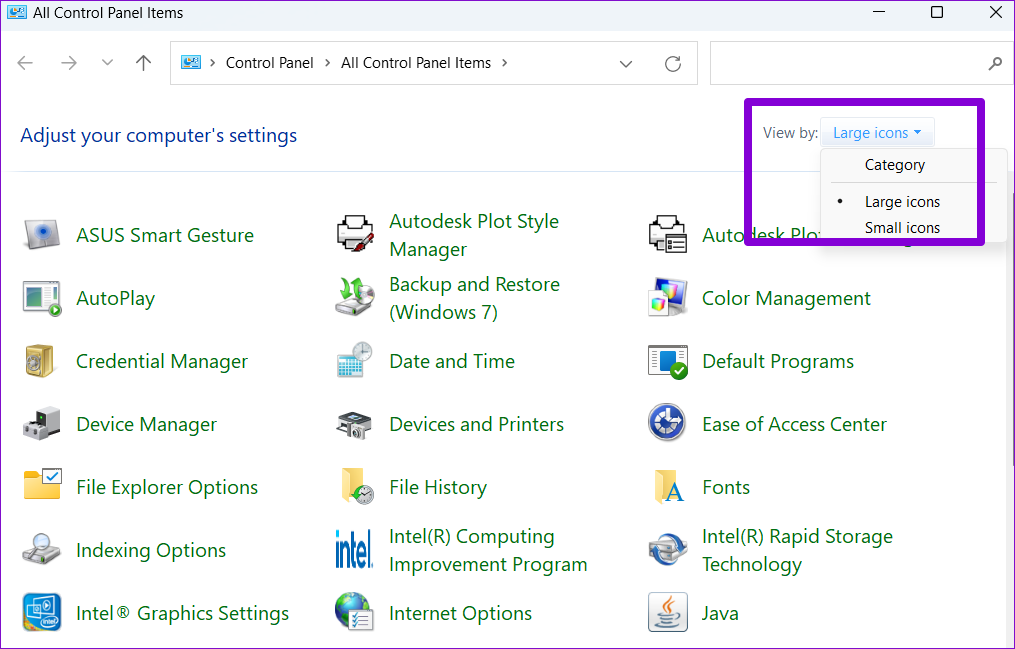
Step 3: Go to Network and Sharing Center.
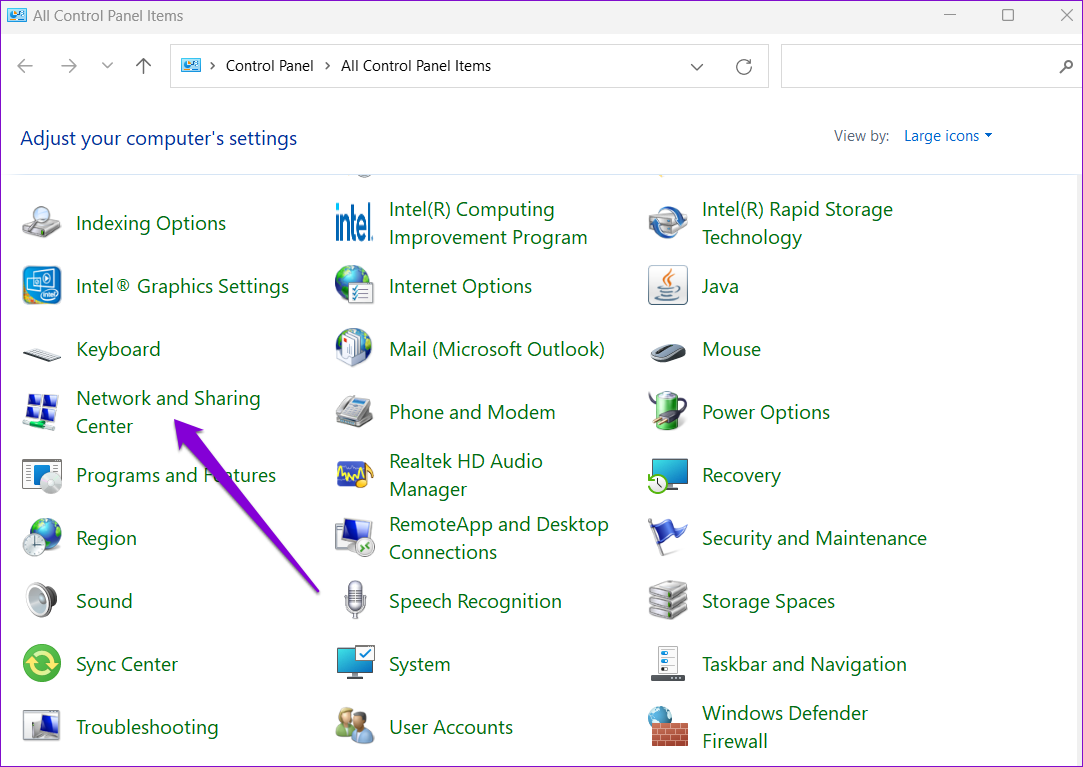
Step 4: Click on Change adapter settings on your left.
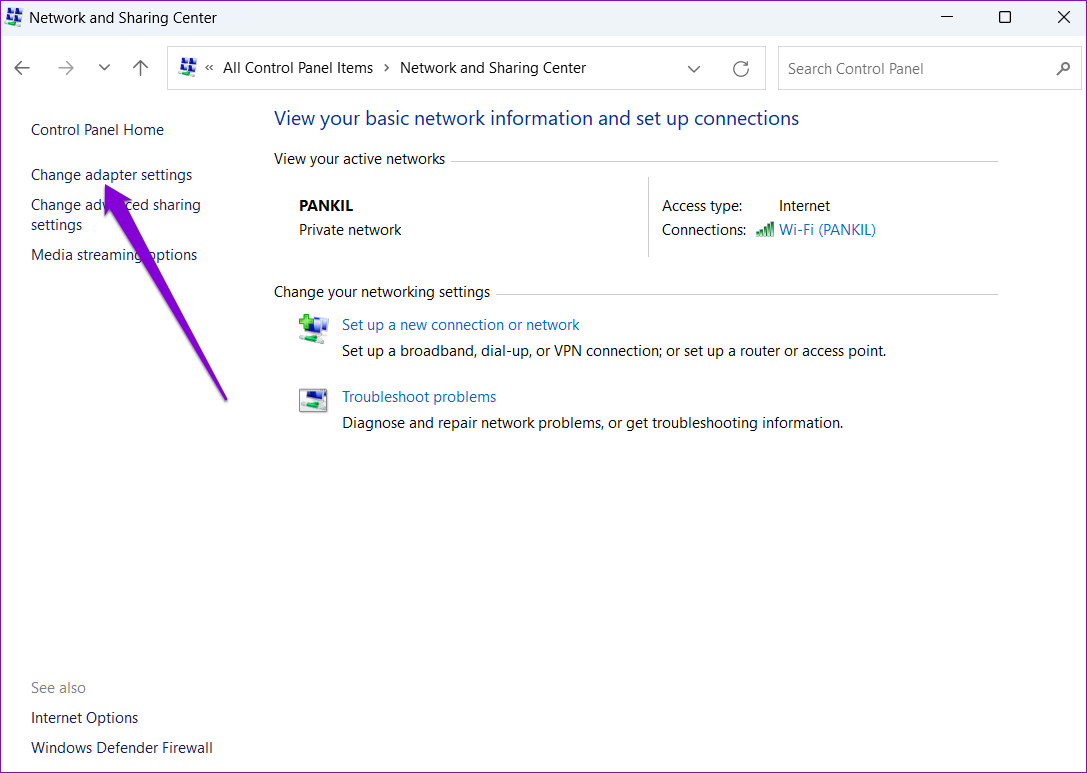
Step 5: Right-click on your internet connection and select Properties.
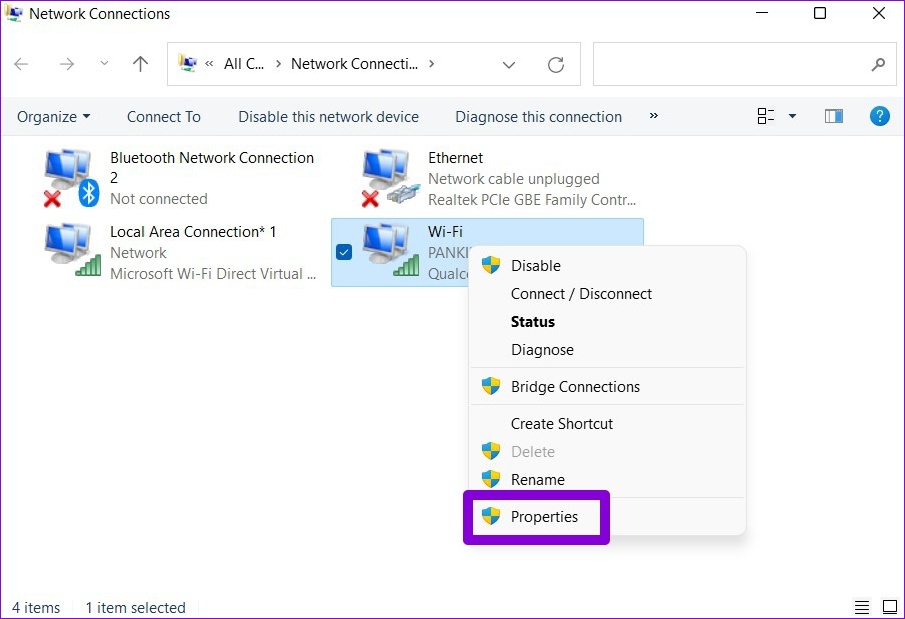
Step 6: Under Networking, double-click on ‘Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)’ to open its Properties.
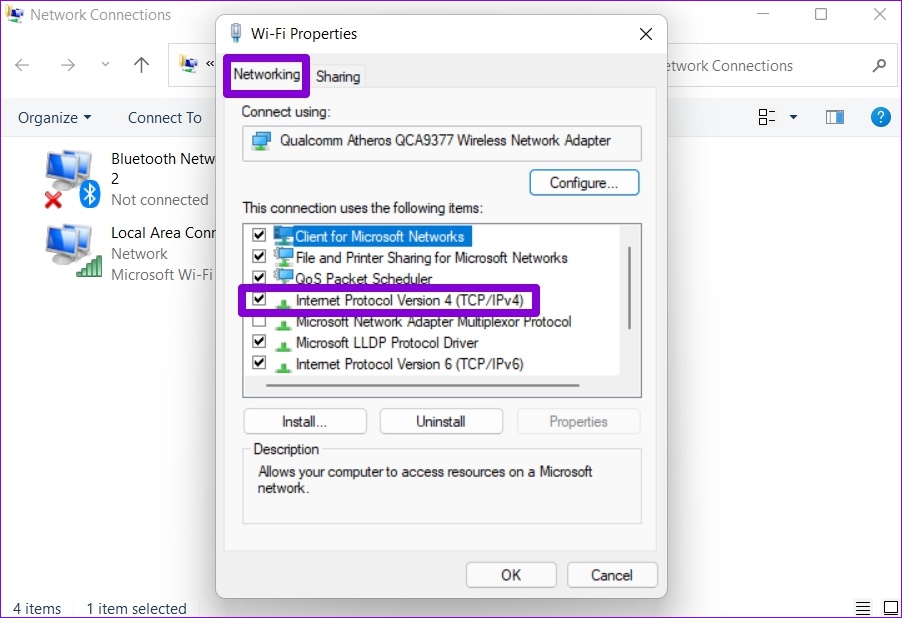
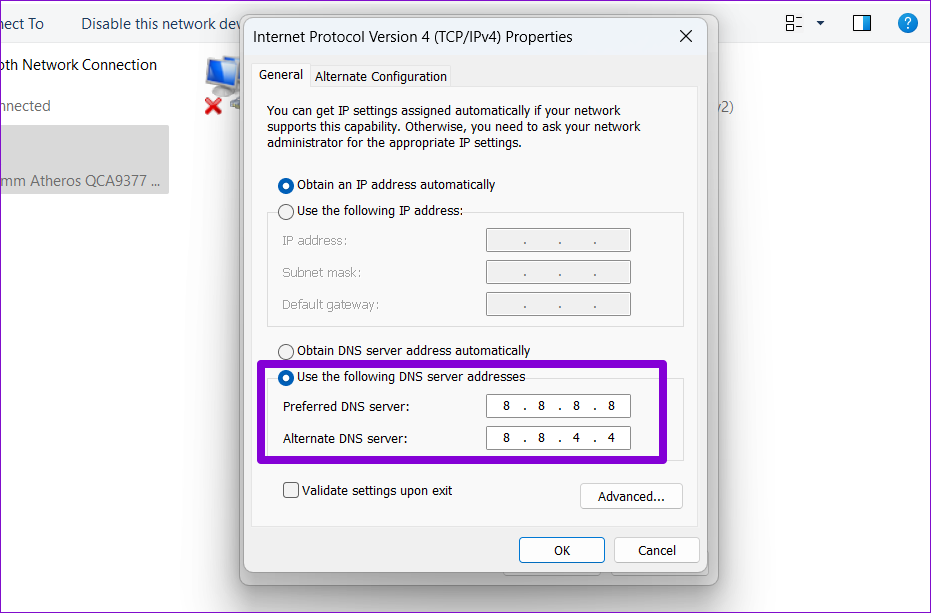
Step 7: Select the ‘Use the following DNS server addresses’ option. Enter primary and secondary DNS addresses in the Preferred DNS Server and Alternate DNS Server fields, respectively.
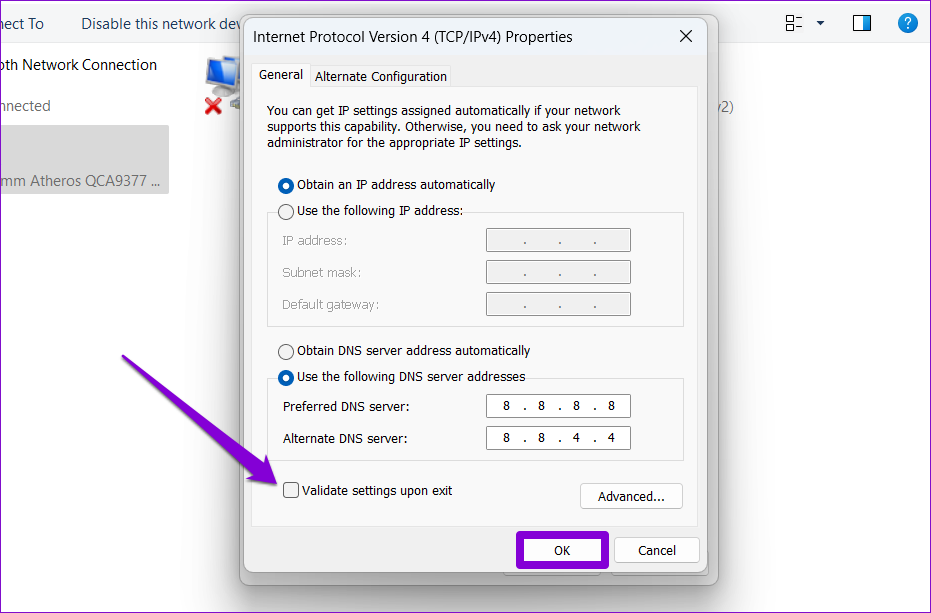
Step 8: Mark the ‘Validate settings upon exit’ box and click on OK.
And you’re good to go. Windows will start using the specified DNS settings immediately.
3. Change DNS Server Using Command Prompt
If you’re a power user who’s familiar with the Command Prompt utility on Windows, you can run a few commands to change the DNS server on your PC. Here’s how.
Step 1: Press the Windows key + S to open Windows Search. Type in cmd and click on Run as administrator.

Step 2: In the console, type the following command and press Enter.
netsh interface show interface
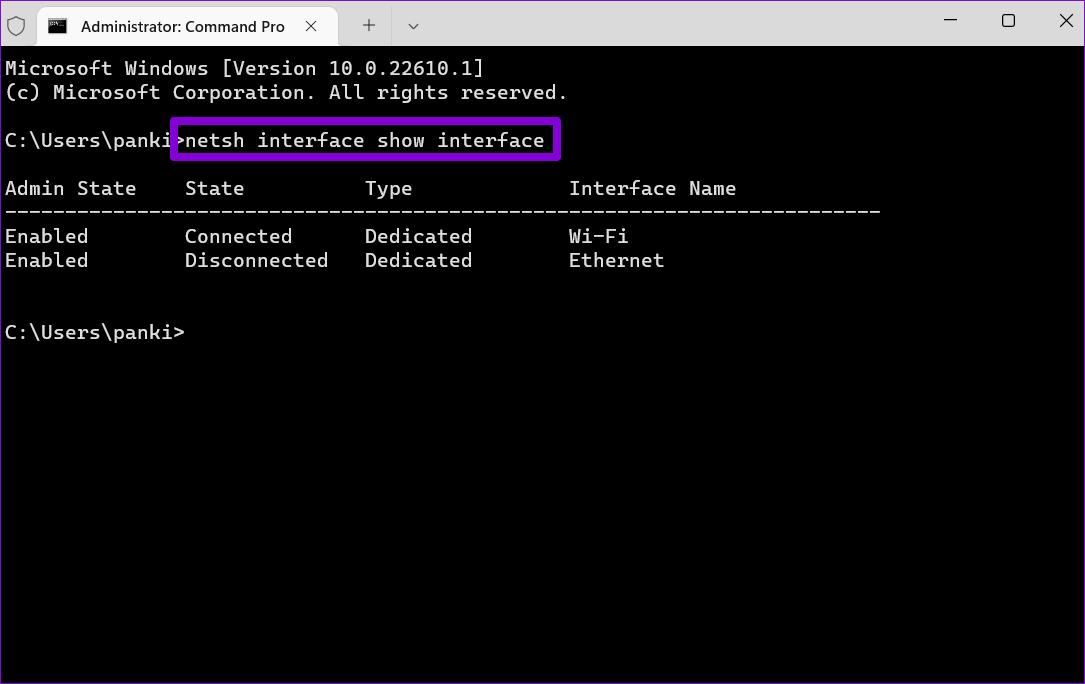
Step 3: Note down the name of your current network connection.
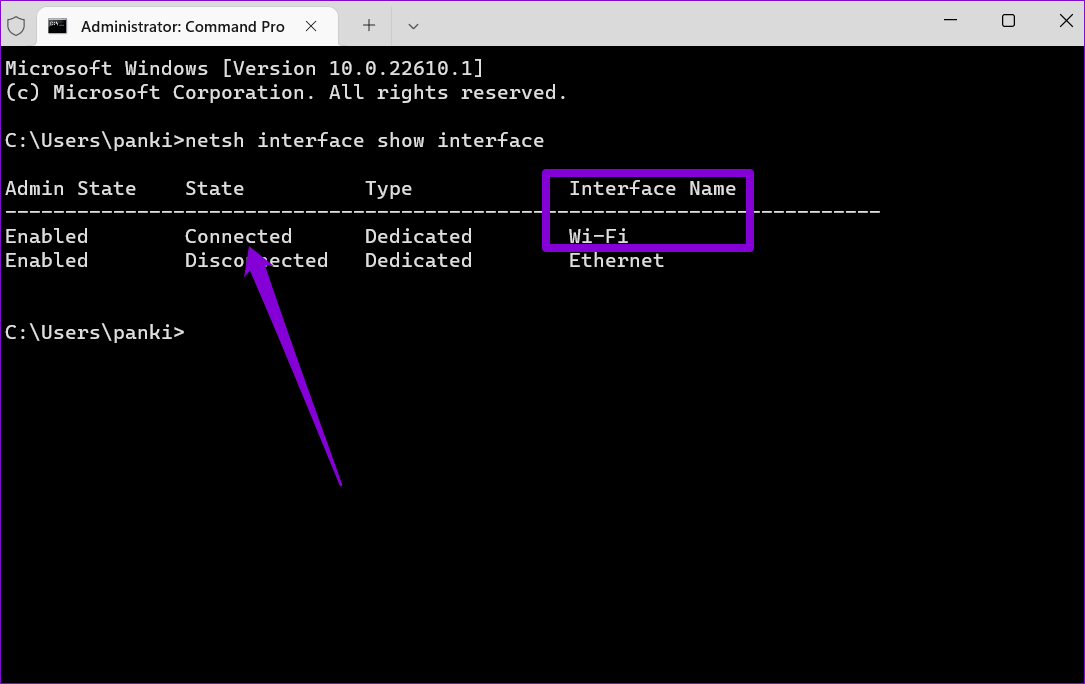
Step 4: Run the following command to set up the primary DNS server.
netsh interface ip set dns name="AdapterName" source="static" address="X.X.X.X"
Replace AdapterName in the above command with the name of your network connection noted in Step 3. Replace X.X.X.X with the actual address of the DNS server you’d like to use.
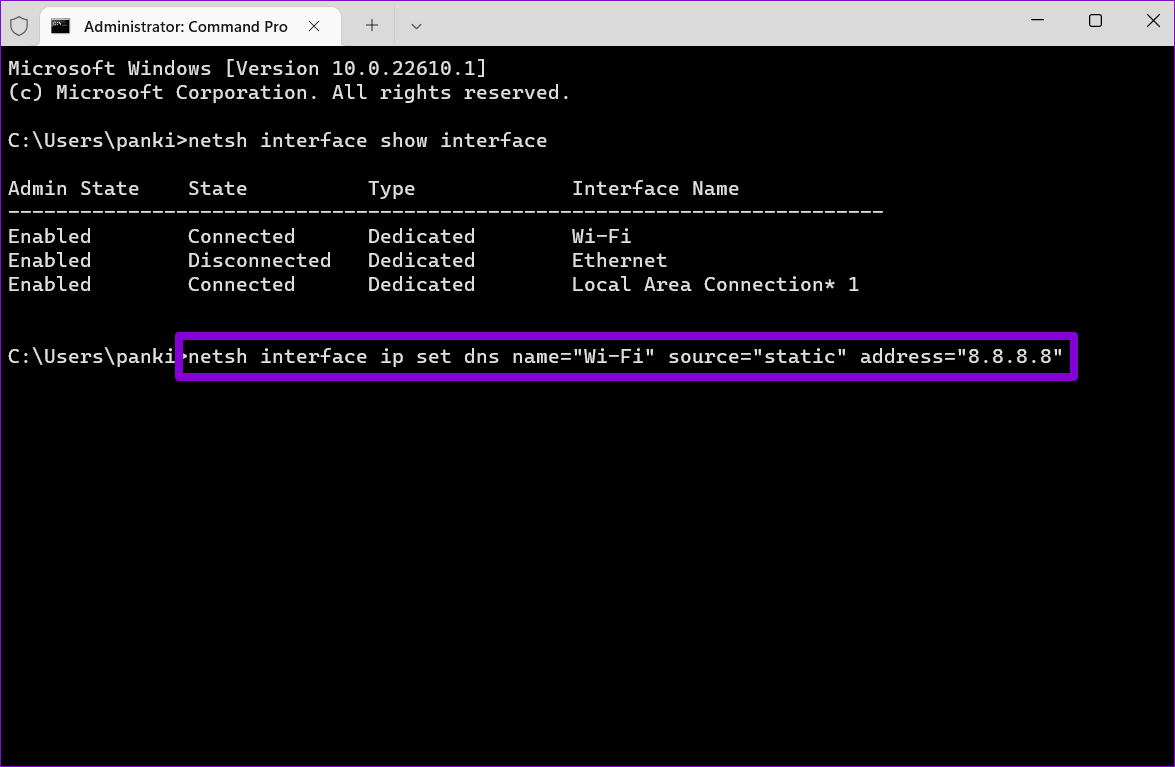
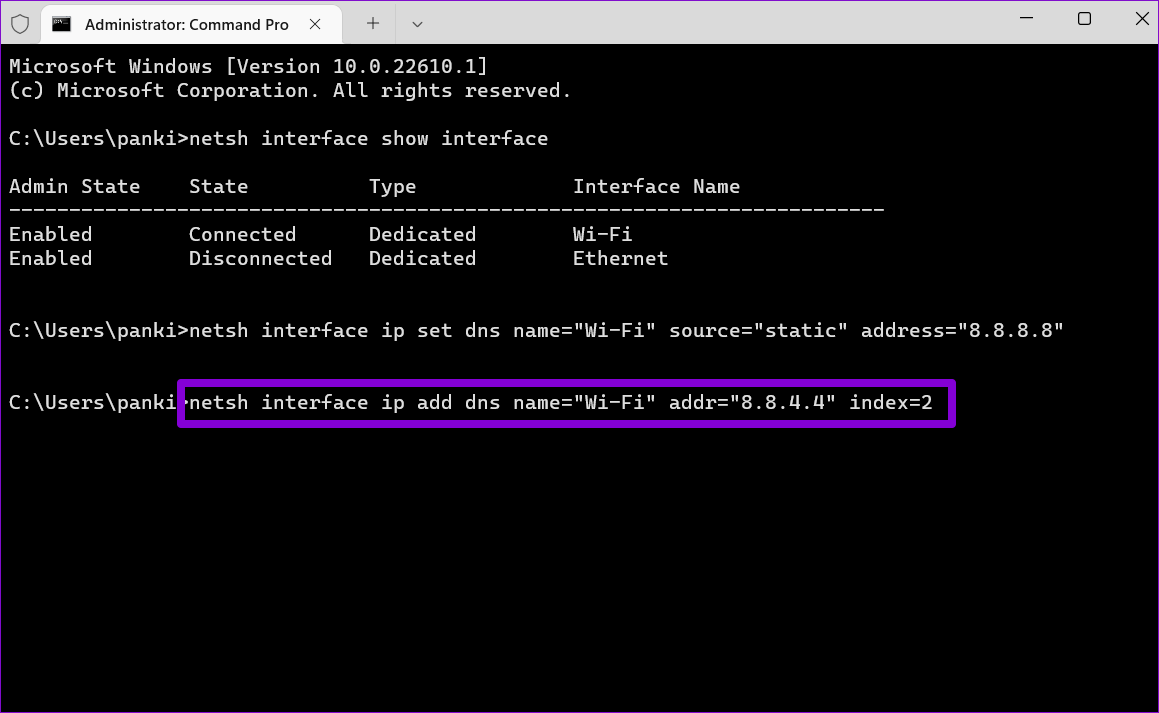
Step 5: Similarly, run the following command to set up an alternate DNS server.
netsh interface ip add dns name="ADAPTER-NAME" addr="X.X.X.X" index=2
Again, replace AdapterName in the above command with the actual name of your network connection. Replace X.X.X.X with the secondary address.
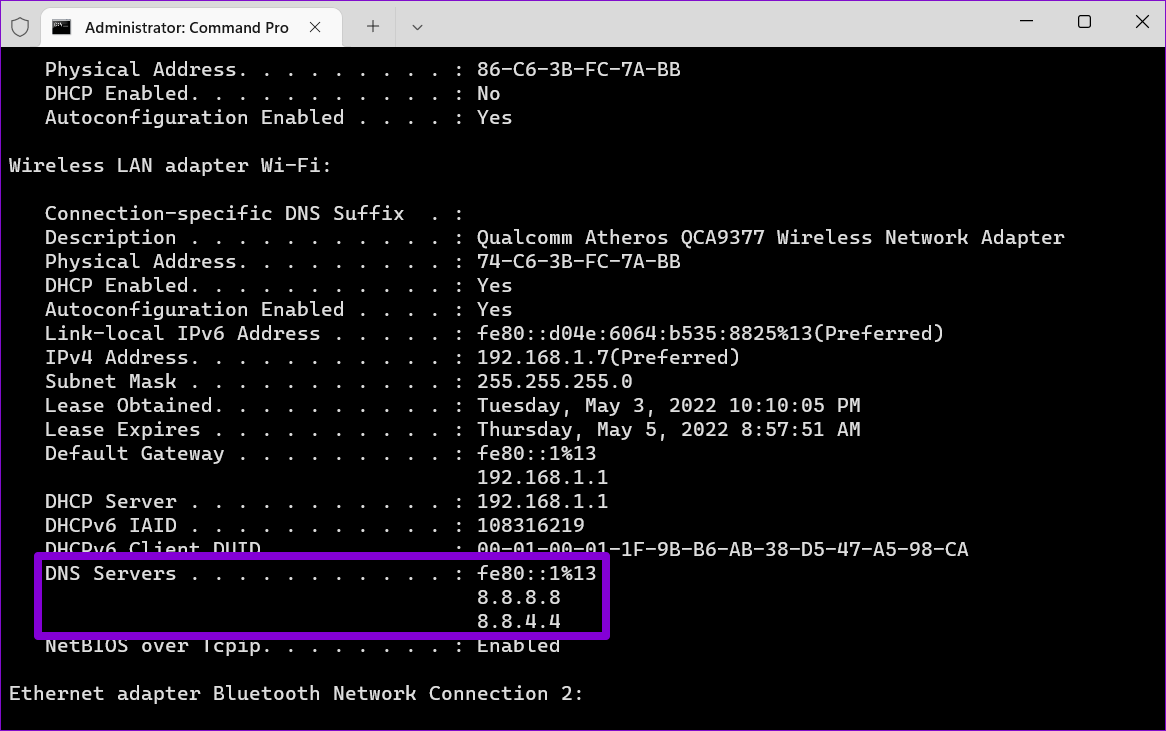
You can confirm the change in the DNS server by viewing your current networking configuration. To do so, run the following command.
ipconfig /all
Time to Switch
Changing DNS servers is something that you may have to do when facing internet connection issues on your PC. And it’s nice to see how Windows offers a few different ways to make that change.
Last updated on 04 May, 2022
The above article may contain affiliate links which help support Guiding Tech. However, it does not affect our editorial integrity. The content remains unbiased and authentic.